Unlocking the Power of Data: The Role of Data Value Realization in Saudi Arabia
In today’s rapidly evolving technological landscape, data has emerged as one of the most valuable assets for individuals, businesses, and governments. As organizations collect and generate increasing amounts of data, the challenge shifts from simply managing that data to harnessing its full potential. In Saudi Arabia, the National Data Management Office (NDMO), under the umbrella of the Saudi Authority for Data and Artificial Intelligence (SDAIA), is leading the way in ensuring that data is managed ethically and strategically, aligning with the goals of Vision 2030. One of the key domains included in the NDMO is the Data Value Realization Domain, which focuses on helping entities derive tangible value from their data.
The Importance of Data Value Realization
As organizations continue to accumulate vast amounts of data, the focus on data value realization has become critical. This concept revolves around extracting actionable insights and business value from data, enabling organizations to make informed decisions and drive growth. Whether in the public or private sector, unlocking the value of data requires strategic planning, robust governance, and adherence to best practices in data management.
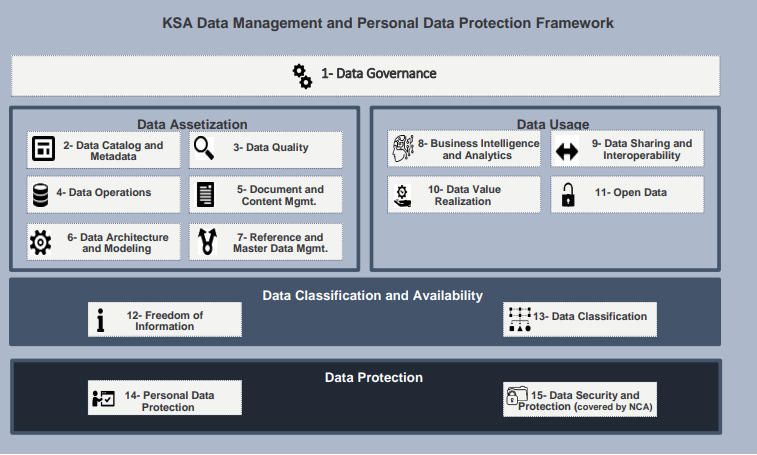
The NDMO’s role in this transformation is pivotal, offering guidance on how to navigate the data landscape. With controls and specifications that cover 15 key domains of data management, the NDMO ensures that the entire data lifecycle—creation, storage, movement, and usage—is optimized to maximize value. Importantly, the NDMO framework mandates that organizations develop clear plans and identify use cases to extract value from data, establishing a data pricing model as part of this approach.
Key Elements of Data Pricing Models
One of the primary components of data value realization is determining the price of data. Whether it is raw data, aggregated information, or specialized data products, pricing models help entities understand the worth of their data in the market. The NDMO outlines specific criteria to consider when pricing data, ensuring fairness and transparency.
Here are the key factors that influence data pricing:
- Data Scarcity:
The availability of the data plays a significant role in its value. Data that is exclusive, rare, or difficult to obtain will generally command a higher price. Whether the data is primary, raw, or available from multiple entities affects its overall market value.
- Diversity of Data Sources:
Data that is collected from multiple, unique sources or linked from different systems is often more valuable. Exclusivity and the complexity of gathering data from diverse sources can increase its worth.
- Number of Customers/Subscribers:
The demand for data by different user segments is another pricing determinant. The broader and more diverse the target audience for the data, the more valuable it becomes.
- Nature of the Data:
Personal data, especially sensitive information, often carries stricter privacy controls, and its pricing reflects this. The nature of the data—whether personal or non-personal, encrypted or unencrypted, aggregated or non-aggregated—will influence how it is priced and traded.
- Type of Data:
Data can be categorized into structured (e.g., databases), semi-structured (e.g., JSON files), or unstructured (e.g., emails, documents). Each type has different complexities and uses, impacting its value.
- Data Size:
Measured in gigabytes or by the number of records, the size of the data also plays a significant role in pricing. Larger datasets may require greater processing power or storage, increasing their cost.
- Price of Similar Data Products in the Market:
A comparative analysis with similar data products in the market helps ensure that pricing remains competitive. Benchmarking the value against market standards is crucial for setting a fair price.
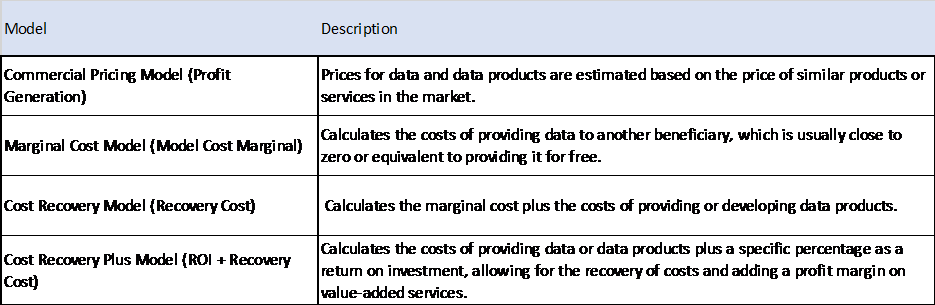
Data Pricing Models
Determining Data Pricing model essential to determine the appropriate price for data achieve revenue from it. The different pricing models which can be considered when developing data products are listed below.
Best Practices for Data Pricing and Value Extraction
To ensure that organizations are fairly pricing their data while maximizing its value, the NDMO has provided a set of best practices. These practices help entities balance the cost of data collection and processing with the potential benefit derived from its use. Following these guidelines allows organizations to establish a sustainable pricing strategy while ensuring they adhere to the NDMO’s controls.
- Align Pricing with Data Type and Effort Expended:
Pricing should reflect not just the data itself but also the effort involved in gathering, cleaning, and processing the information. High-quality, refined data may come at a premium compared to raw, unstructured data.
- Ensure Transparency and Fairness:
Data pricing models must be transparent and based on objective criteria to prevent arbitrary pricing. This also ensures that customers and data consumers understand the value they are receiving.
- Leverage Use Cases for Maximum Value:
Identifying specific use cases that benefit from the data is essential for extracting value. Organizations should assess how their data can be applied in various contexts, from predictive analytics and decision-making to market insights and operational efficiencies. - Continuous Review and Adaptation:
As the data landscape evolves, so must pricing models. Continuous evaluation of the data’s relevance, demand, and market conditions is necessary to adapt pricing strategies accordingly.
TCG’s Data Value Realization Expertise
TCG offers comprehensive solutions to help clients unlock the full value of their data:
- Monetization Use Case Identification: Identifying innovative ways to turn data into revenue streams.
- Data Pricing Models: Creating strategic pricing models based on data rarity, demand, and market conditions.
- Data Value Roadmap: Guiding clients from data collection to value extraction with a clear action plan.
- Data Integration: Connecting various data sources to boost usability and value.
- Data Quality Improvement: Ensuring high data accuracy and readiness for market use.
- Compliance Assurance: Guaranteeing adherence to NDMO regulations for ethical, legal, and secure data management.